Home > Press > Quantum researchers cause controlled ‘wobble’ in the nucleus of a single atom
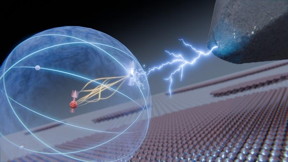 |
| Researchers from Delft University of Technology in The Netherlands have been able to initiate a controlled movement in the very heart of an atom. They caused the atomic nucleus to interact with one of the electrons in the outermost shells of the atom. This electron could be manipulated and read out through the needle of a scanning tunneling microscope. The research, published in Nature Communications today, offers prospects for storing quantum information inside the nucleus, where it is safe from external disturbances. Credit TU Delft |
Abstract:
Researchers from Delft University of Technology in The Netherlands have been able to initiate a controlled movement in the very heart of an atom. They caused the atomic nucleus to interact with one of the electrons in the outermost shells of the atom. This electron could be manipulated and read out through the needle of a scanning tunneling microscope. The research, published in Nature Communications today, offers prospects for storing quantum information inside the nucleus, where it is safe from external disturbances.
Quantum researchers cause controlled ‘wobble’ in the nucleus of a single atom
Delft, Netherlands | Posted on September 13th, 2024For weeks on end, the researchers studied a single titanium atom. “A Ti-47 atom, to be precise,” says research leader Sander Otte. “It has one neutron less than the naturally abundant Ti-48, which makes the nucleus slightly magnetic.” This magnetism, the ‘spin’ in quantum language, can be seen as a sort of compass needle that can point in various directions. The orientation of the spin at a given time constitutes a piece of quantum information.
Precisely tuned
The nucleus of an atom floats inside a – comparatively – giant void far away from the orbiting electrons, oblivious of its environment. But there is one exception: due to the extremely weak ‘hyperfine interaction’, the nuclear spin can be influenced by the spin of one of the electrons. “Easier said than done,” says Lukas Veldman, who recently defended his PhD dissertation on the research with honours. “The hyperfine interaction is so weak that it is effective only in a very small, precisely tuned magnetic field.”
Voltage pulse
Once all experimental conditions were met, the researchers used a voltage pulse to push the electron spin out of equilibrium, after which both spins wobbled together for a fraction of a microsecond. “Exactly how Schrödinger predicted,” says Veldman. Alongside the experiments he performed calculations that reproduced the observed fluctuations surprisingly well. The strong agreement between observations and predictions demonstrates that no quantum information is lost during the interaction between electron and nucleus.
Storing quantum information
The efficient shielding from the environment makes the nuclear spin a viable candidate for holding quantum information. The current research may bring that application one step closer. But that is not what primarily drives the researchers. Otte: “This experiment gives humans influence on the state of matter on an unimaginably small scale. To me, that alone makes it worth the effort.”
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Pauline Bijster
Delft University of Technology
h.p.bijster@tudelft.nl
Copyright © Delft University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
Quantum Physics
Imaging
![]() Turning up the signal November 8th, 2024
Turning up the signal November 8th, 2024
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() New ocelot chip makes strides in quantum computing: Based on "cat qubits," the technology provides a new way to reduce quantum errors February 28th, 2025
New ocelot chip makes strides in quantum computing: Based on "cat qubits," the technology provides a new way to reduce quantum errors February 28th, 2025
![]() New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
![]() Researchers observe “locked” electron pairs in a superconductor cuprate August 16th, 2024
Researchers observe “locked” electron pairs in a superconductor cuprate August 16th, 2024
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Leading the charge to better batteries February 28th, 2025
Leading the charge to better batteries February 28th, 2025
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() New ocelot chip makes strides in quantum computing: Based on "cat qubits," the technology provides a new way to reduce quantum errors February 28th, 2025
New ocelot chip makes strides in quantum computing: Based on "cat qubits," the technology provides a new way to reduce quantum errors February 28th, 2025
Tools
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
![]() New 2D multifractal tools delve into Pollock's expressionism January 17th, 2025
New 2D multifractal tools delve into Pollock's expressionism January 17th, 2025
![]() Turning up the signal November 8th, 2024
Turning up the signal November 8th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Researchers succeed in controlling quantum states in a new energy range December 13th, 2024
Researchers succeed in controlling quantum states in a new energy range December 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








