Home > Press > With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters
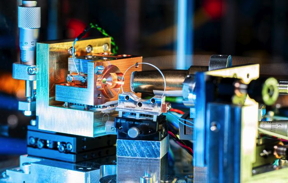 |
| VECSEL setup for the development of a low-noise pump source for quantum frequency conversion CREDIT © Fraunhofer IAF |
Abstract:
The expansion of fiber optics is progressing worldwide, which not only increases the bandwidth of conventional Internet connections, but also brings closer the realization of a global quantum Internet. The quantum internet can help to fully exploit the potential of certain technologies. These include much more powerful quantum computing through the linking of quantum processors and registers, more secure communication through quantum key distribution or more precise time measurements through the synchronization of atomic clocks.
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters
Freiburg, Germany | Posted on April 5th, 2024However, the differences between the glass fiber standard of 1550 nm and the system wavelengths of the various quantum bits (qubits) realized to date represent a hurdle, because those qubits are mostly in the visible or near-infrared spectral range. Researchers want to overcome this obstacle with the help of quantum frequency conversion, which can specifically change the frequencies of photons while retaining all other quantum properties. This enables conversion to the 1550 nm telecom range for low-loss, long-range transmission of quantum states.
Project HiFi: Enabling technologies for quantum frequency conversion
In the joint project “HiFi — Highly integrated quantum frequency converter of highest fidelity based on innovative laser, fiber and production technology” funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), researchers are working on the realization of all necessary technologies to provide quantum frequency converters (QFK) with high efficiency and low noise for initial test tracks. The Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF has contributed to the project with the successful development of disk lasers (also known as vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting lasers, VECSELs) based on gallium antimonide (GaSb). These are optically pumped, surface-emitting semiconductor lasers with an external resonator and intracavity filter for wavelength selection.
2.4 W output power with absolute frequency stability below 100 kHz
“The VECSELs we developed as part of HiFi are spectrally narrow-band pump sources which, depending on the output wavelength of the qubits used, specifically cover a wavelength between 1.9 and 2.5 µm and achieve an output power of up to 2.4 W with an absolute wavelength stability of less than 2 fm. This corresponds to a frequency stability of less than 100 kHz and clearly falls below the frequency stability class 1E-9. The result represents an international record for this type of laser,” explains Dr. Marcel Rattunde, HiFi sub-project coordinator and head of the optoelectronics department at Fraunhofer IAF.
“The result was made possible by the close cooperation with project partner MENLO Systems GmbH. Together, we locked the disk laser to a frequency comb, which in turn was coupled to a 10 MHz reference,” emphasizes Rattunde.
In their experiments, the researchers set the emission wavelength exactly to the target wavelength for demonstration experiments at the fiber link of Saarland University (2062.40 nm), to which Fraunhofer IAF has handed over the laser module. In addition to power scaling, the most important research tasks of Fraunhofer IAF in the HiFi project are the precise understanding of the mode behavior of the lasers and the identification and elimination of noise sources.
Quantum frequency conversion using pump lasers
In quantum frequency conversion, the energy of the pump photon is subtracted from the signal photon by a difference frequency process in a non-linear optical crystal. To ensure a low-noise process, the energy of the pump photons must be below the target wavelength (usually 1550 nm), otherwise the pump laser can generate photons in the output signal due to parasitic effects.
In combination with the MENLO frequency comb, the VECSELs developed at Fraunhofer IAF meet the high requirements of quantum frequency conversion, as their narrow bandwidth and wavelength stability prevent fluctuations in the pump wavelength and consequently changes in the target wavelength of the qubits. If there is a deviation above the natural linewidth, the qubits would no longer be indistinguishable, which would eliminate a basic requirement for subsequent quantum mechanical processing.
Fraunhofer IAF at Photonics Europe 2024
From April 7 to 11, 2024, Fraunhofer IAF researchers will present their latest research results in the field of optoelectronics at this year’s SPIE Photonics Europe in Strasbourg.
Steffen Adler will talk about the HiFi project results on April 11 at 2 pm in his presentation “High-power 2 μm GaSb-based VECSEL with an absolute wavelength stability below 1 MHz”.
All presentations at a glance:
Marko Härtelt: “Multiplexed dual-core QCL-based sensor for real-time standoff-spectroscopy in crime scene investigations” (April 8, 4:30 p.m., Schuman, Level 1)
Thorsten Passow: “Optimization of AlGaAs-based Bragg-reflection waveguides for entangled photon sources” (9 April, 18:10, Galerie Schweitzer, Level 0)
Peter Holl: “Light Source based on Adiabatic Frequency Conversion in Whispering Gallery Resonators tailored for holographic metrology” (April 10, 10:00 a.m., Rome, Level 0)
Steffen Adler: “High-power 2 μm GaSb-based VECSEL with an absolute wavelength stability below 1 MHz” (April 11, 14:00, Dresde/Salon 13, Level 1)
Further information
Program of SPIE Photonics Europe 2024: https://spie.org/conferences-and-exhibitions/photonics-europe/programme/browse-programme#_=_
Optoelectronics at Fraunhofer IAF: https://www.iaf.fraunhofer.de/en/researchers/optoelectronic-devices.html
HiFi project profile: https://www.iaf.fraunhofer.de/en/researchers/optoelectronic-devices/Hifi.html
####
About Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics
The Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF is one of the world's leading research institutions in the fields of III-V semiconductors and synthetic diamond. Based on these materials, Fraunhofer IAF develops components for future-oriented technologies, such as electronic circuits for innovative communication and mobility solutions, laser systems for real-time spectroscopy, novel hardware components for quantum computing as well as quantum sensors for industrial applications. With its research and development, the Freiburg research institute covers the entire value chain — from materials research, design and processing to modules, systems and demonstrators. www.iaf.fraunhofer.de/en
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Armin Müller
Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics
armin.mueller@iaf.fraunhofer.de
Office: +49 761 5159 670
Copyright © Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
Quantum Physics
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Quantum communication
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() New ocelot chip makes strides in quantum computing: Based on "cat qubits," the technology provides a new way to reduce quantum errors February 28th, 2025
New ocelot chip makes strides in quantum computing: Based on "cat qubits," the technology provides a new way to reduce quantum errors February 28th, 2025
![]() New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
![]() Quantum researchers cause controlled ‘wobble’ in the nucleus of a single atom September 13th, 2024
Quantum researchers cause controlled ‘wobble’ in the nucleus of a single atom September 13th, 2024
![]() Researchers observe “locked” electron pairs in a superconductor cuprate August 16th, 2024
Researchers observe “locked” electron pairs in a superconductor cuprate August 16th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Announcements
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Bringing the power of tabletop precision lasers for quantum science to the chip scale December 13th, 2024
Bringing the power of tabletop precision lasers for quantum science to the chip scale December 13th, 2024
![]() Researchers succeed in controlling quantum states in a new energy range December 13th, 2024
Researchers succeed in controlling quantum states in a new energy range December 13th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








